A gas-fluid level is the most typical imaging finding. however, it is only present in 25-50% of patients with acute sinusitis 4. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (fess) has revolutionised the approach and treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis. certain anatomical variations are thought to be predisposing factors for the development of sinus disease and it is necessary for the surgeon to be aware of these variations, especially if the patient is a candidate for fess 10. Mar 29, 2020 · a sinus x-ray helps doctors detect problems with the sinuses. sinuses are normally filled with air, so the passages will appear black on an x-ray of healthy sinuses. a gray or white area on an. Nov 15, 2002 · plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. possible findings in acute sinusitis include mucosal thickening, air-fluid levels, and complete opacification of the involved.
Sinus Xray Purpose Procedure And Risks
Cysts are represented by soft-tissue opacity with a surface convex towards the cavity of the sinus, along any of the walls. the role of imaging in acute sinusitis is controversial, and many regard acute sinusitis a clinical penaksiran. mucosal thickening is seen in more than 90% of patients with sinusitis, but this finding is highly nonspecific. Fever, headache, postnasal discharge of thick sputum, nasal congestion and an abnormal sense of smell. acute sinusitis is a clinical diagnosis characterized by symptom duration of less than 4 weeks 11.
See full list on radiopaedia. org. Conservative medical treatment until the inflammation subsides and treatment of the cause, e. g. dental caries. if it becomes chronic sinusitis, functional endoscopic sinus surgerymay be considered. 1. erosion through bone 1. 1. subperiosteal abscess 1. 1. 1. frontal sinus superficially (pott puffy tumor) 1. 1. dua. frontal or ethmoidal sinuses into the orbit (subperiosteal abscess of the orbit) dua. dural venous sinus thrombosis 3. intracranial ray sinusitis x finding in extension 3. 1. meningitis 3. 2. subdural empyema 3. 3. cerebral abscess. See full list on emedicine. medscape. com. A characteristic feature on ct sinuses is sclerotic thickened bone (hyperostosis) involving the sinus wall from a prolonged mucoperiosteal reaction. intrasinus calcificationmay be present. the presence of opacification is not a good distinguisher from an acute sinus infection. there are five main patterns of chronic inflammatory disease that classify the disease into distinct anatomical/pathological groups and are dependent on the drainage pathways affected. this classification helps the surgeon to select the type of surgery needed 12: 1. ostiomeatal complex pattern: maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid air cells, and frontal sinuses are affected due to obstruction of the ostiomeatal complex 2. infundibular pattern: isolated obstruction to the ethmoid infundibulum and/or maxillary sinus ostium tiga. sphenoethmoidal recess pattern: inflammatory changes in the sphenoethmoidal recess obstruct the sphenoid sinus in isolation or in conjunction with the posterior ethmoidal air cells 4. sinonasa
It is worth noting is no definite correlation between symptoms and imaging findings of chronic sinusitis and that endoscopic chronic sinusitis may have no imaging correlation as the mucosa is best appreciated on the former 11. Chronic sinusitis is defined clinically as a sinonasal infection lasting more than 12 weeks. patients may present with symptoms of sinusitis such as nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, facial pain, headache, halitosis, anosmia, etc. it is worth noting is no definite correlation between symptoms and imaging findings of chronic sinusitis and that endoscopic chronic sinusitis may have no imaging correlation as the ray sinusitis x finding in mucosa is best appreciated on the former 11. Li z, wang x, jiang h, qu x, wang c, chen x, et al. chronic invasive fungal rhinosinusitis vs sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma: the differentiating value of mri. eur radiol. 2020 aug. 30 (8):4466-4474. jeon y, lee k, sunwoo l, et al. deep learning for diagnosis of paranasal sinusitis using multi-view radiographs. A sinus x-ray helps doctors detect problems with the sinuses. sinuses are normally filled with air, so the passages will appear black on an x-ray of healthy sinuses. a gray or white area on an.
Mengenal Kista Endometriosis Kehamilan Apakah Kondusif
More x ray finding in sinusitis images. The most common radiographic maxillary sinus finding was mucosal thickening, followed by mucous cysts and occupation of the whole sinus. conventional ct can be considered a reliable method for the diagnosis of maxillary sinus pathology. Plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. possible findings in acute sinusitis ray sinusitis x finding in include mucosal thickening, air-fluid levels, and complete opacification of the involved.
Sinus x-ray: purpose, procedure, and risks.
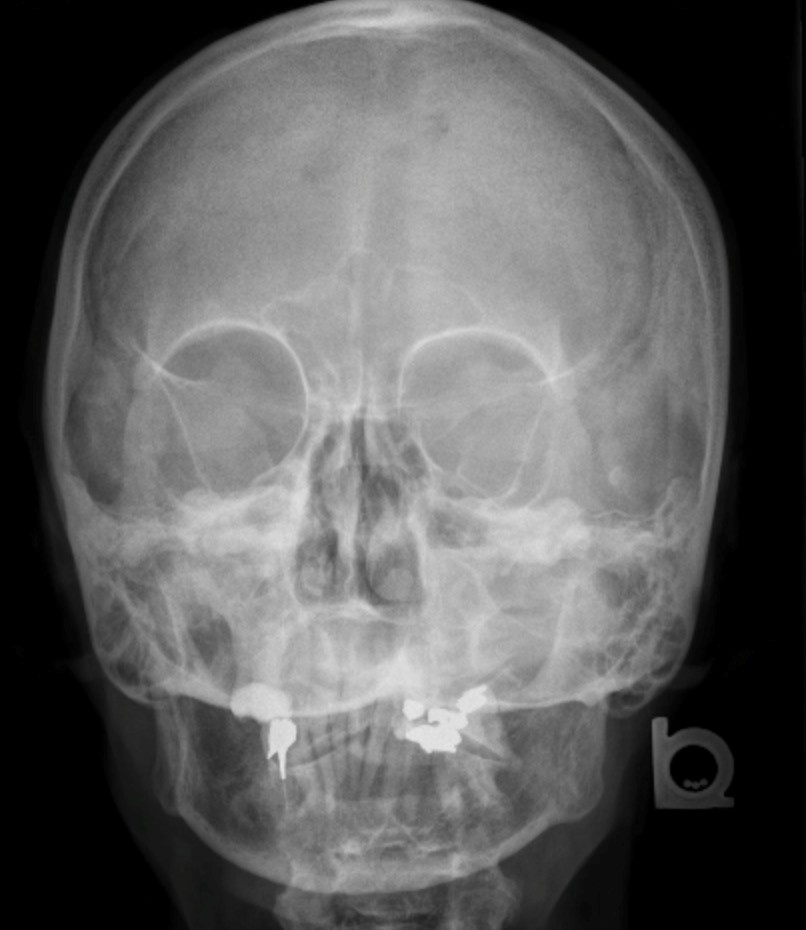
What do x-rays for sinusitis show? orlando ent.
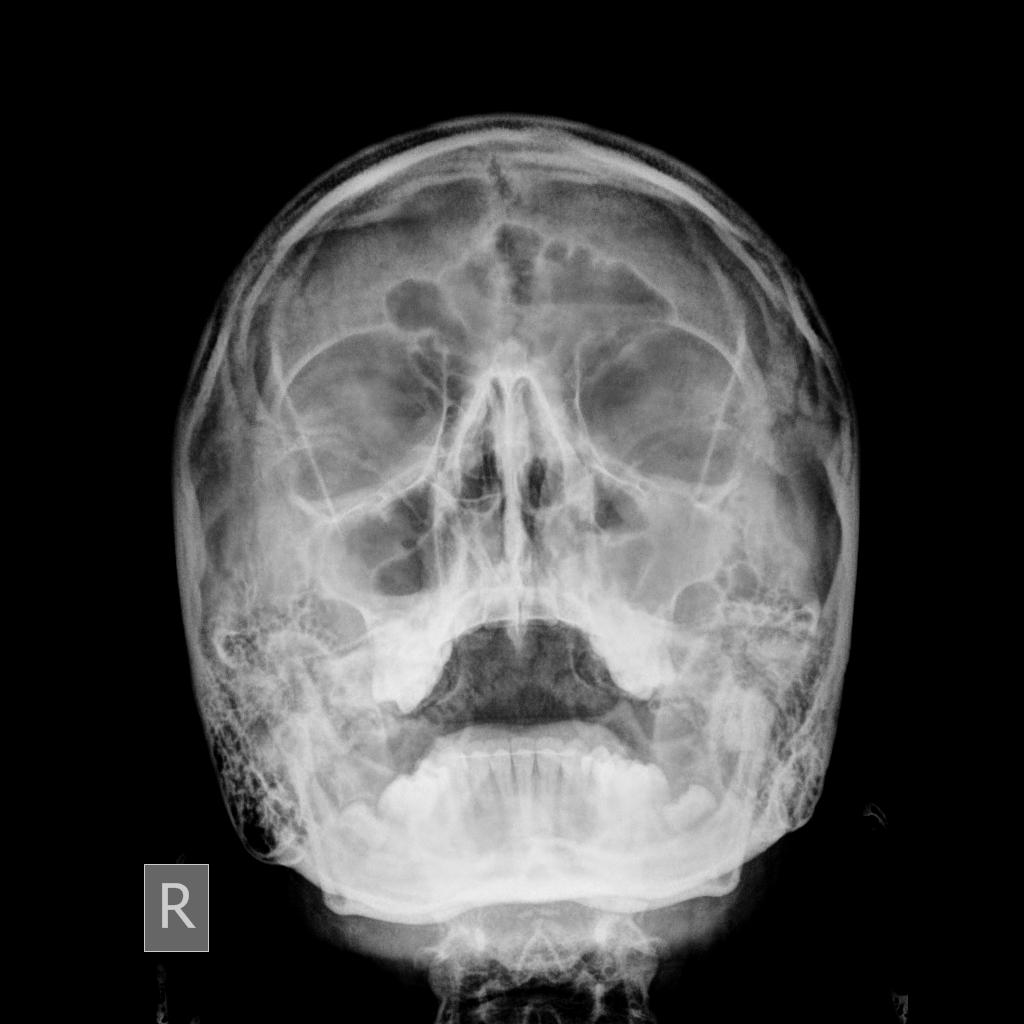
To evaluate the pattern of sinusitis, one must understand the drainage of various sinuses. the anatomy of drainage revolves around the ostiomeatal unit, which is not a single morphologic structure but a combination of the following structures: 1. middle turbinate 2. ethmoid bulla 3. uncinate process 4. maxillary infundibulum 5. hiatus semilunaris (ie, space beneath the middle turbinate) 6. maxillary os the hiatus semilunaris is a space between the uncinate process (anteroinferiorly) and the ethmoid bulla (posterosuperiorly). the anterior group of ethmoid air cells drains into the anterior aspect of the hiatus semilunaris through the frontonasal duct. the middle group drains into the hiatus semilunaris on or above the ethmoidal bulla. the frontal sinus drains through the frontonasal duct or through the anterior ethmoidal cells into the hiatus semilunaris. the maxillary infundibulum drains into the posterior part of the hiatus semilunaris. the frontal, maxillary, anterior, and middle Imaging findings are nonspecific and can be seen in a large number of asymptomatic patients (up to 40%) 11. imaging findings should be interpreted with clinical and/or endoscopic findings. a gas-fluid level is the most typical imaging finding. however, it is only present in 25-50% of patients with acute sinusitis 4. opacification of the sinuses and gas-fluid level best seen in the maxillary sinus. it does not allow assessment of the extent of the inflammation and its complications. the most common method of evaluation. better anatomical delineation and assessment of inflammation extension, causes, and complications. peripheral mucosal thickening, gas-fluid level in the paranasal sinuses, gas bubbles within the fluid and obstruction of the ostiomeatal complexesare recognized findings. rhinitis, often associated with sinusitis, is often characterized by thickening of the turbinates with obliteration of the surrounding air channels. this should not be confused with the normal nasal cyc X-rays are a common diagnostic tool for identifying broken bones, which may first come to mind, but it’s also useful in evaluating the possibility of sinusitis. sinusitis is inflammation or infection in the sinus facial cavity, the area surrounding the nose, eyes, and cheeks inside the skull. Usually following a viral upper respiratory tract infection. dental caries, periapical abscess and oroantral fistulation lead to a spread of infection to the maxillary sinus. cystic fibrosisand allergy are risk factors. other anatomical variants that may predispose to the inflammation include nasal septal deviation, a spur of the nasal septum and/or frontoethmoidal recess variants. patients in an intensive care ray sinusitis x finding in setting are at an increased risk of acute sinusitis. risk factors identified include 10: 1. indwelling nasogastric tubes and/or endotracheal tubes 1. 1. especially nasotracheal routing dua. prolonged duration on the unit tiga. younger age.
Posting Komentar untuk "Ray Sinusitis X Finding In"